Self-assembled monolayer of push-pull chromophores towards the polarization modulation for controlled detection of biomolecules
Junlong Wang 1, irginie Gadenne1, Jean-Manuel Raimundo2, Lionel Patrone1
1Aix Marseille Univ, Université de Toulon, CNRS, ISEN Méditerranée, IM2NP UMR 7334, 83000 Toulon, France
2Aix-Marseille Univ., CNRS, CINaM, Marseille, France 2
The specific detection of antibodies using antibody/antigen binding interactions has been the subject of numerous studies in the field of biosensors [1-3]. Notably, a promising functional ON/OFF system has been proposed based on the reversible modification of the conformation of a charged oligopeptide by the application of an electrical potential on the surface, thus making it possible to control the antibody-antigen interaction [4]. So far, this system can only respond to a single electrical stimulus, thus limiting its use to a single antibody/antigen pair and preventing the detection of the binding interaction of several antibody/antigen pairs within a single platform. For this purpose, we are considering an original approach based on the use of “push-pull” chromophores to control the potential allowing the conformation of the oligopeptide to be switched between the OFF state (antibody-antigen interaction not allowed) and the ON state (interaction permitted). This structure of the push-pull chromophores forms an electrical dipole depending on the nature of the donor and attractor groups, and the π-conjugated bridge. The idea is to add push-pull chromophores presenting different electrical dipole moments - each one being associated to a specific electrical potential value - between the surface and the oligopeptide supporting a given antigen, and to insert these systems within an inert matrix of molecular compound of oligoethylene glycol (OEG) (Figure). Therefore in this work we have synthesized original non-charged push-pull chromophores bearing a thiol anchroring group, and studied their self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on gold surfaces. After having analysed the influence of the various parameters (e.g. solvent, concentration,…) on the quality of homogeneous push-pull films, we have devoted our work to the preparation of SAMs made of isolated push-pull chromophores inside the OEG inert matrix testing various approaches and parameters. The next step will address first the strategy of grafting of an oligopeptide on top of the isolated push-pull chromophores, and second the study of the push-pull dipole effect on the voltage enabling to unfold the oligopeptide to activate the ON state of the sensor.
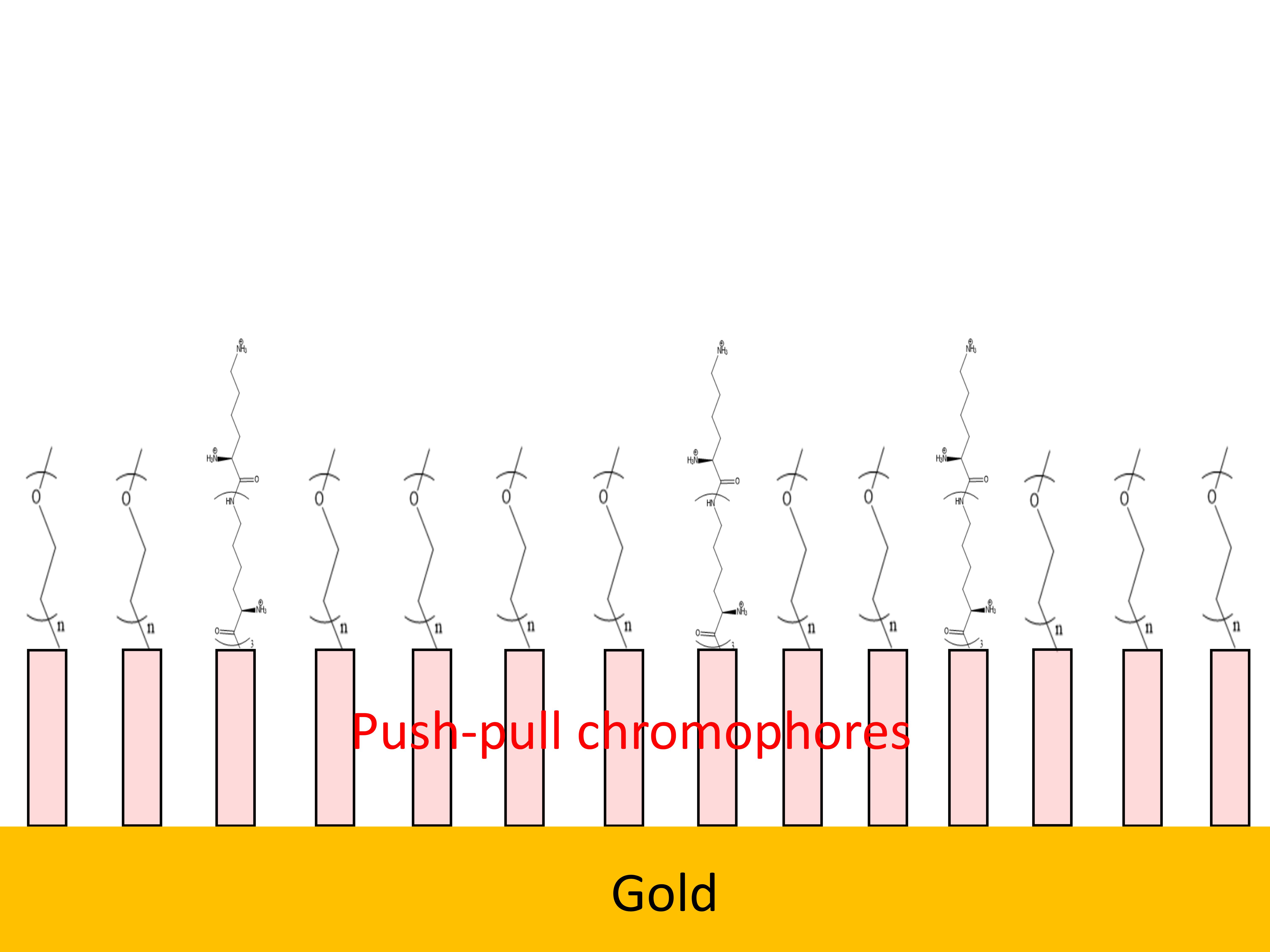
The structure of molecular films using push-pull chromophore with modulated polarization for the controlled detection of biomolecules
References:
1. Casalini, et al., ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5051
2. Marquette, C.A.; Blum, L.J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 1424
3. Wen, W. et al., Anal.Chem. 2017, 89, 138
4. Santos Gomes, B. et al., ACS Appl.Bio.Mater., 2018, 1, 738

